
The Cottage Cheese vs Greek Yogurt debate is a big one in the health community. Ever stand in the dairy aisle wondering which one is actually better for you? You’re not alone. They’re both nutritional powerhouses, packed with protein and perfect for everything from a quick breakfast to a healthy snack.
But they have some major differences when it comes to key nutrients like sodium, gut-friendly probiotics, and even the type of protein they contain. So, let’s settle the debate once and for all.
They’re both nutritional powerhouses, but if you want an even deeper dive into the numbers, you can check out our full guide to Cottage Cheese Macros .
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
The Quick Answer: Which is Healthier?
For a quick answer, Greek yogurt is generally healthier due to its higher probiotic content and significantly lower sodium. However, cottage cheese often packs slightly more protein per serving, making it a great choice for muscle building. The best option depends on your specific dietary needs, such as improving gut health or maximizing protein intake.
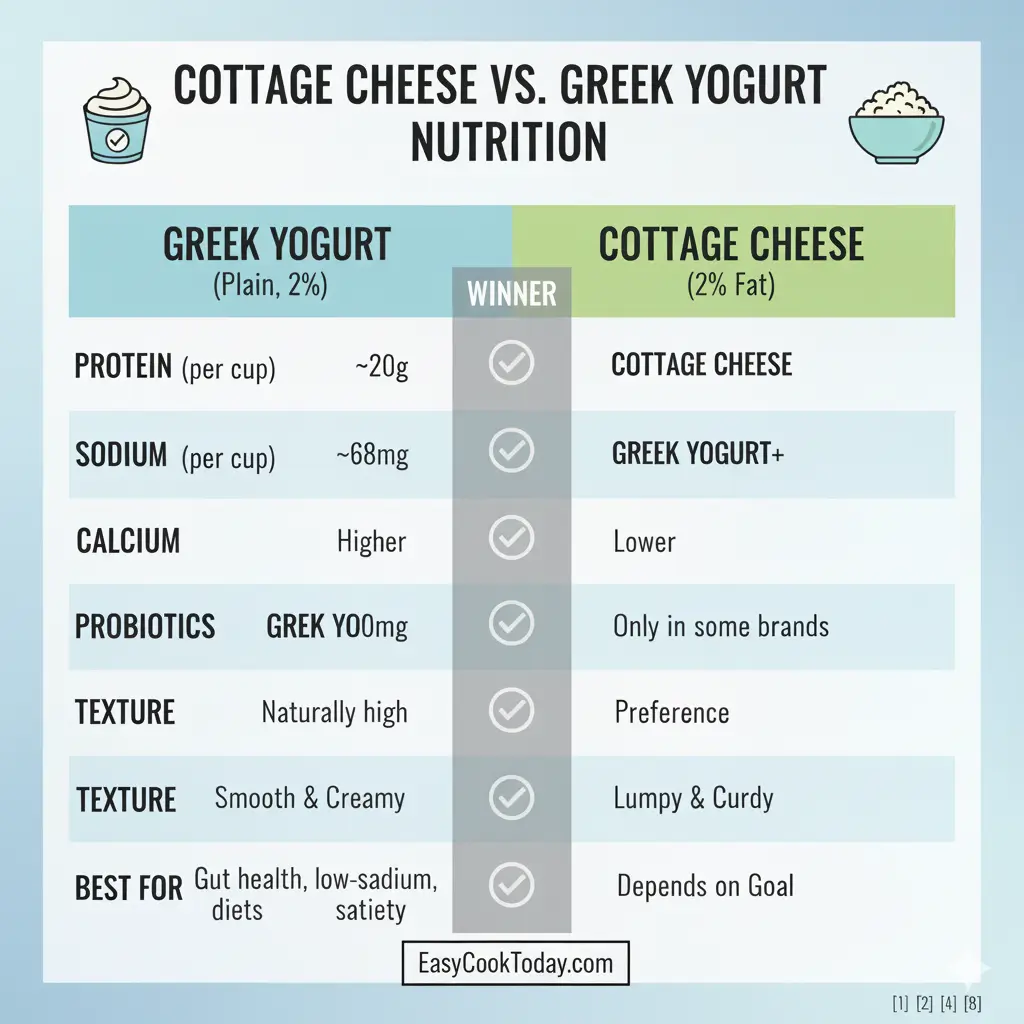
Cottage Cheese vs. Greek Yogurt: Nutritional Showdown
For a true side-by-side look, nothing beats a simple table. Here’s how a standard one-cup serving of 2% milkfat cottage cheese and plain 2% Greek yogurt stack up, based on data from the USDA FoodData Central database.
| Feature | Greek Yogurt (Plain, 2%) | Cottage Cheese (2% Fat) | Winner |
| Protein (per cup) | ~20g | ~24g | Cottage Cheese |
| Sodium (per cup) | ~68mg | ~700mg+ | Greek Yogurt |
| Calcium | Higher | Lower | Greek Yogurt |
| Probiotics | Naturally high | Only in some brands | Greek Yogurt |
| Texture | Smooth & Creamy | Lumpy & Curdy | Preference |
| Best For | Gut health, low-sodium diets | Maximizing protein, satiety | Depends on Goal |
The Case for Greek Yogurt vs. Cottage Cheese
Greek yogurt’s smooth texture and tangy flavor make it incredibly versatile, but its nutritional profile is where it truly shines for specific goals.
Choose Greek Yogurt if:
- You are monitoring your sodium intake. With less than 10% of the sodium found in most cottage cheese brands, Greek yogurt is the clear winner for a heart-healthy diet, helping you stay below the American Heart Association’s sodium recommendations.
- You want to improve your gut health. It’s packed with live and active cultures (probiotics) that are fantastic for digestion and overall gut wellness.
- You need a smooth base. It’s the perfect substitute for sour cream or mayonnaise in dips, sauces, and dressings.
When to Choose Cottage Cheese
Cottage cheese has made a huge comeback, and for good reason. Its lumpy texture might not be for everyone, but its protein content is hard to beat. Its unique texture and high protein also make it a popular choice in Italian cooking, though it has key differences when you compare Cottage Cheese vs. Ricotta.
Choose Cottage Cheese if:
- Your primary goal is the absolute highest protein count. It generally has a few more grams of protein per serving, which is a big reason it ranks so well in our high protein foods comparison. This can make a real difference for athletes or anyone focused on muscle building.
- You want to stay full longer. The majority of its protein is casein, a slow-digesting protein that promotes a feeling of fullness (satiety) for hours.
- You prefer a milder flavor. It’s less tangy than Greek yogurt, making it a great blank canvas for both sweet and savory toppings.
Creative Ways to Use Greek Yogurt and Cottage Cheese
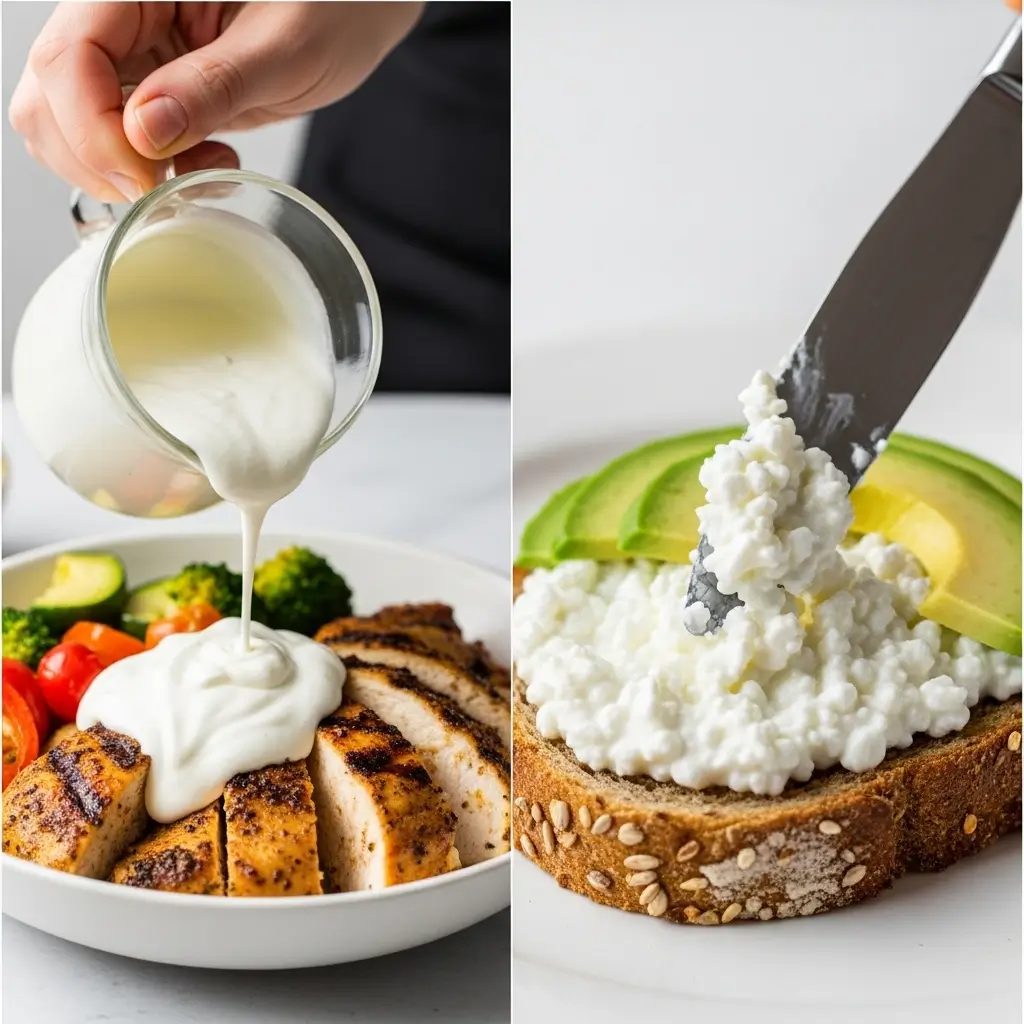

Knowing the nutritional differences is one thing, but putting them to use in your kitchen is what it’s all about. Here are some simple, delicious ideas to get you started.
Easy Recipe Ideas for Greek Yogurt:
Beyond a simple parfait, Greek yogurt is a versatile secret weapon in both sweet and savory dishes.
- Healthy Cream Sauce for Pasta: Stir a dollop of plain Greek yogurt into your warm pasta sauce to add creaminess without the heavy cream.
- Tenderizing Marinade: The lactic acid in yogurt is fantastic for tenderizing chicken or lamb. Mix it with lemon juice, garlic, and herbs for an amazing marinade.
- 2-Ingredient Bagel Dough: Mix equal parts plain Greek yogurt and self-rising flour to create a simple, high-protein dough for bagels, pizza crust, or flatbreads.
- Sour Cream Substitute: Use it as a 1:1 replacement for sour cream on tacos, baked potatoes, or in dips to cut fat and boost protein.
Creative Recipe Ideas for Cottage Cheese:
Think beyond just a scoop with fruit. Modern cottage cheese recipes are all about texture and protein.
- Creamy Scrambled Eggs: Whisk a few tablespoons of cottage cheese into your eggs before scrambling. They’ll be incredibly fluffy, creamy, and packed with extra protein.
- High-Protein Mac and Cheese: Blend cottage cheese with a little milk until smooth, then stir it into your favorite mac and cheese recipe. It adds a protein punch and amazing creaminess.
- Blended Veggie Dip: For a super-smooth, high-protein dip, blend cottage cheese with roasted red peppers or a packet of ranch seasoning.
- The Viral Cottage Cheese Ice Cream: Blend a cup of cottage cheese with a tablespoon of maple syrup and some melted chocolate, then freeze until firm. It’s a game-changing healthy dessert.
Shopping Guide: How to Pick the Best Product
The dairy aisle can be overwhelming. Here’s what to look for on the label to make sure you’re getting the best quality product.
- Check the Milkfat Percentage:
- Full-Fat (5%): The creamiest and most satisfying. Great for keto diets or if you want a richer flavor.
- Low-Fat (2%): A great middle-ground that balances flavor and lower fat content. This is the most common and versatile option.
- Non-Fat (0%): The leanest option, but often has a tangier, less creamy texture. Some brands add thickeners or gums to improve the mouthfeel.
- Always Choose “Plain”:
- Flavored yogurts and cottage cheeses are often loaded with added sugars that can rival a candy bar. It’s always better to buy plain and add your own fresh fruit, honey, or toppings. You control the sweetness and avoid processed ingredients.
- Look for “Live and Active Cultures”:
- For Greek yogurt, this is the key to getting those probiotic gut-health benefits. The label should clearly state it contains live cultures. For cottage cheese, some brands (like Good Culture) are now adding probiotics, which will be listed on the front of the tub.
Can I Substitute One for the Other in Recipes?
While you can sometimes swap them, you need to be careful.
- Substituting Greek Yogurt for Cottage Cheese: This is easier. For dips or sauces, you can often make this swap, but the result will be tangier. If the recipe calls for blended cottage cheese, Greek yogurt is an excellent substitute.
- Substituting Cottage Cheese for Greek Yogurt: This is trickier due to the high sodium content and lumpy texture. You should only do this in recipes where the cottage cheese is blended smooth first. Be prepared to reduce the salt in the rest of your recipe, as cottage cheese will add a significant amount of its own.
By keeping these tips in mind, you can confidently choose the right product for your health goals and culinary needs, making the most of these two dairy powerhouses.
Cottage Cheese vs Greek Yogurt: Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is cottage cheese or Greek yogurt better for weight loss?
Both are excellent for weight loss! Their high protein content helps keep you full, reducing the urge to snack. Because it’s lower in sodium and can reduce bloating, some people slightly prefer Greek yogurt, but you can’t go wrong with either.
2.Can I eat Greek yogurt or cottage cheese on a keto diet?
Yes, in moderation. Choose plain, full-fat versions of both. A half-cup serving of either can easily fit into a ketogenic diet, but be mindful of the carb count, which is usually around 5-8 grams per serving.
3. Why is cottage cheese so high in sodium?
Salt is a key ingredient in making cottage cheese. It’s added during production to help separate the curds from the whey and acts as a natural preservative and flavor enhancer. You can look for “low-sodium” or “no salt added” varieties if this is a concern.
4. Which one tastes better?
This is purely personal preference! If you love a rich, tangy, and perfectly smooth texture, you’ll prefer Greek yogurt. If you like a milder, saltier, and more textured (chunky) experience, you’ll probably love cottage cheese.
The Final Verdict
You can’t make a bad choice here. Both Greek yogurt and cottage cheese are fantastic, nutrient-dense foods.
- For an all-around health boost, especially for gut health and low sodium, reach for the Greek yogurt.
- For maximum protein and long-lasting fullness, grab the cottage cheese.
So, in the great Cottage Cheese vs Greek Yogurt showdown, the winner is clear: it depends on your goals. The best strategy is to keep both in your fridge and choose the one that best fits your meal for the day.
Print
The Viral 5-Minute Savory Cottage Cheese Bowl
- Total Time: 5 minutes
- Yield: 1 serving
Description
Think cottage cheese is just for fruit? Think again. This savory cottage cheese bowl is your new high-protein favorite — bursting with flavor from chili crisp oil and creamy egg yolk, ready in under 5 minutes.
Ingredients
- 1 cup good-quality cottage cheese (2% or 4% fat for the best flavor and texture)
- 1 soft-boiled or ‘jammy’ egg
- 1–2 teaspoons chili crisp oil (use more or less depending on your spice preference)
- 1 teaspoon toasted sesame seeds
- 1 tablespoon thinly sliced scallions (green parts only) or fresh chives
- Optional: A pinch of flaky sea salt
Instructions
- Spoon the cottage cheese into a bowl and create a small well in the center.
- Slice the soft-boiled egg in half and place it yolk-side up into the well.
- Drizzle chili crisp oil generously over the entire bowl, ensuring some crunchy bits on top.
- Sprinkle with toasted sesame seeds and scallions or chives.
- Add a pinch of flaky sea salt if desired and enjoy immediately!
Notes
Add avocado for extra creaminess, Everything Bagel seasoning or chopped almonds for crunch, and fresh cucumber or cherry tomatoes for a veggie boost. No chili crisp? Try olive oil, red pepper flakes, and lemon juice instead.
- Prep Time: 5 minutes
- Cook Time: 0 minutes
- Category: Breakfast
- Method: No Cook
- Cuisine: Fusion
